We have been working with Machine Learning models, cooking raw data into golden features for the models. Including me, we have been doing stuff manually and we also have been questioning where to put cooked features properly, like in our local machine? We have heard there is a Feature Store as a savior with tons of new concepts and functionalities, but there are two common concerns we have all been through:
- How to use it seamlessly?
- We desire more, but what are our expectations?
Quick access:
The rewind
Ok first let’s go through what we already know about feature store.

What are the features in Machine Learning?
As we know, features are characteristic of a specific entity (user, merchant, promotion, etc..) in the real world at a specific time. Features can be derived from raw data and transformed in various ways, such as scaling, normalization, or aggregation, to improve the quality and consistency of the data.
A feature is a data point with the following criteria:

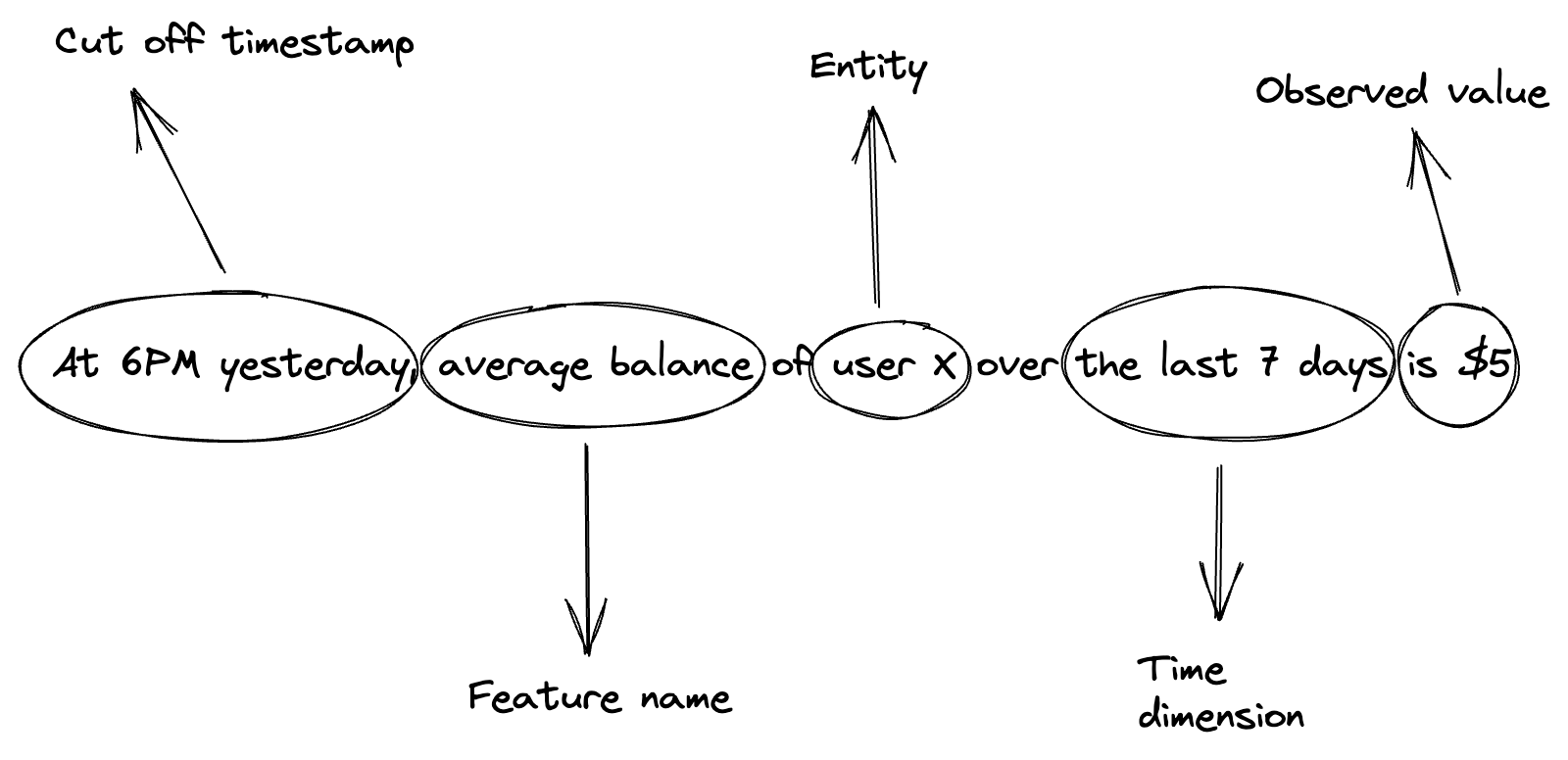
entity is obviously the first thing we should look at, this is a primary object we’re working on to collect data from. The cut off timestamp determines the latest timestamp at which the data of an entity is considered valid for feature calculation. Any data beyond this specific timestamp is excluded before performing feature calculations.

Cut Off Timestamp illustration (Source: Featuretools documentation)
Observed value is calculated from the extracted data (Data points), usually combined with Aggregation methods to produce a single value as a summarization of what happened back then. Optionally, the time dimension is also needed to fulfill the characteristic of the target entity. For example:
Features play a crucial role in machine learning, they expose complex patterns from entities, such as user transaction behaviour, for ML models to learn and make predictions. The quality of features mostly has a major impact on the performance of a model. We obviously met this term Garbage in garbage out since the day we involved in the ML world. As a result, Data Scientists usually spend significant time and effort, back and forth selecting and engineering features.
So, What is the feature store?
As it’s called, a feature store is an abstract layer working as a place where all features are stored and can be served from. Feature store makes sure users can get the features correctly as defined above, without duplication.
Technically, a feature store is combined by sub-components which are well defined in this blog. We can see each one manage a corresponding flow to end up serving features in various ways to meet users’ needs, with additional management ability.
Where do we place it in our data ecosystem?

As it stands between data warehouses and ML jobs, it brings more ability and benefits to the team as well as leadership in terms of:
- Data storage: A centralized place to store features, produced from other upstream data sources. The data source can be either relational databases or distributed data storage systems, such as Hadoop or Spark. Feature store streamlines the operations to get raw data ready for being processed and transformed into features.
- Feature management: Tools for organizing, versioning, and managing features, including the ability to track changes and compare versions of features.
feature discoveryandfeature registryhelp team members can explore, comprehend, and reuse features built by each other, which saves dedicated work from the members and reduce duplicated data produced by individuals. Meanwhile, integrating consistent materialization flow from the feature store is also supported in good practice across teams. - Feature access and retrieval: Interfaces are provided to easily retrieve features for batch processing or in low latency for (near) real-time prediction based on a particular situation.
- Monitoring and performance: Tools for monitoring the performance of features, including metrics such as feature usage, processing times, and model accuracy.
The long-term impact
Consequently, the team can have more capable of focusing on other critical parts. For example:
- Data governance: more well-organized data from feature store helps the organization to keep track of data access and permissions, including the ability to enforce security and privacy policies.
- Business analysis: by pruning time-consuming tasks, there will be more room for conducting analysis in deep with less distraction from engineering stuff.
- Pipeline optimization: With the independence of feature store, we can less care where we have to produce clean data to fit into feature engineering pipelines. There is always more room for optimization in deep to save operational and computational costs by pursuing better data engineering practices (data lakehouse, query engine, etc..) to serve the data in a more efficient way.
The state
Thanks to the promising functionalities feature stores provide, it is gaining attraction from organizations to implement into their ML system, but most of the time there is still a struggle that stakeholders find hard to start implementing the component.
Various new concepts to get familiar for both managers and team members, in order to finalize a true north to follow. More collaboration will be also required, based on the new concepts, to make things work smoothly.
For example: collaborative feature engineering, it’s the ability to conduct customization on sharable features transformation and computations to extend existing features to build more advanced features for the team.
Another example is, features should be defined consistently by everyone in the team, this helps others quickly catch up with the previous works. It’s been a pain point for feature store because as of now it is not possible to track the lineage of any derived features and monitor its usage.
Conclusion
To summarize, we all agreed that feature store is necessary but we desire more from it, which are usability, comprehensibility and reliability. As of now, this still needs to be involved a lot of manual work.
However, in the last few months, there has been a significant evolution of feature store to grow into a Feature Engineering Platform, or in short, Feature Platform. In part two, we will look at the resolution it has to resolve the above concerns.